Monthly Archives: December 2006
Linchpin Discovered in Insulin Metabolism; Gene May Contribute to Development of Type 2 Diabetes
Scientists from the new interdisciplinary LIMES (Life & Medical Sciences) Centre at the University of Bonn have identified a new gene which could play an important role in the development of diabetes.
Study: Obesity Linked to Increased Kidney Disease Risk in Type 1 Diabetes
For patients with type 1 diabetes, obesity is an important risk factor for the development of diabetic kidney disease, reports a study in the January Journal of the American Society of Nephrology.
Video Gaming Puts Children More At-Risk for Behavioral and Health Problems
Video game makers seem to be addressing concerns about how playing affects children. But too much gaming still puts children more at-risk for behavioral and health problems, health experts say.
Poll: Obesity Cited Number-One Kids’ Health Issue: Americans Split on Who’s Responsible
Obesity or being overweight is seen as the most important health issue for U.S. children, according to a new poll.
Drug Treatment Slows Macular Vision Loss in Diabetics
A drug commonly used to slow the loss of central vision has shown promise in stemming a common precursor of blindness in diabetics, which involves the same central light-sensitive area of retina,.
Recall Alert: FDA Updates its Nationwide Alert on Counterfeit One Touch Blood Glucose Test...
FDA is alerting the public to counterfeit blood glucose test strips being sold in the US for use with various models of LifeScan, Inc., One Touch Brand Blood Glucose Monitors.
Study: Odds Are That Gamblers Have More Health Problems
People who gamble at least five times a year have more health problems than people who gamble less frequently, a new study reveals.
New Data Confirms Protocol to Reverse Type 1 Diabetes
New data published in "Science" provide further support for a protocol to reverse type 1 diabetes in mice and new evidence that adult precursor cells from the spleen can contribute to the regeneration of beta cells.
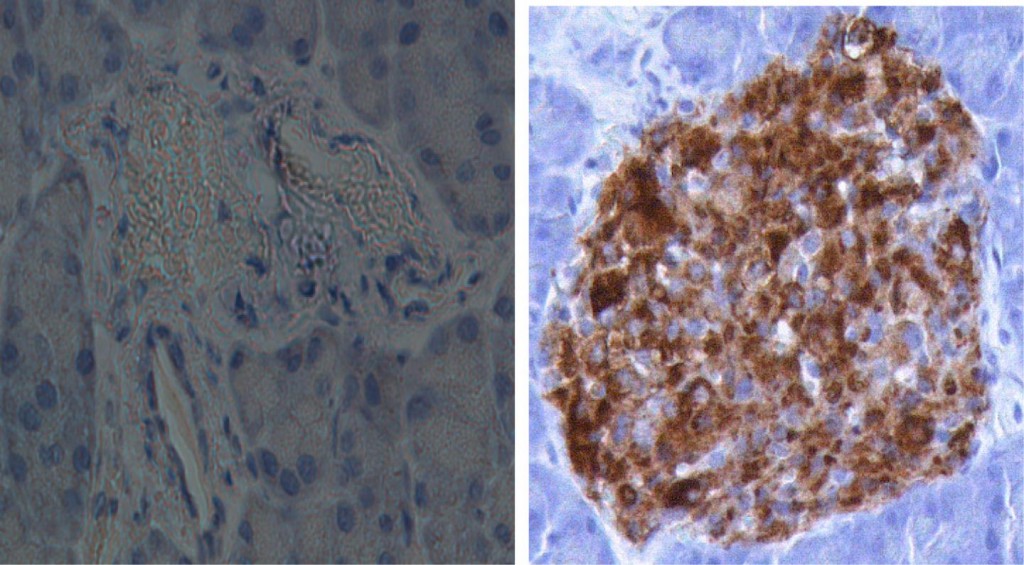
Research Yields New Insights Into The Cause Of Diabetes
The cause of insulin-dependent, permanent, diabetes in newborn babies may be a deficiency in the enzyme Pancreatic Endoplasmic Reticulum Kinase (PERK) during a critical period of development before birth.
Study: Treatment With Certain Anti-Hypertensive Drugs May Reduce Alzheimer’s Disease
A new cardiovascular drug screening has identified existing anti-hypertensive agents capable of preventing cognitive decline and amyloid neuropathology associated with Alzheimer's disease.
Researchers: Statin Users Risk Heart Attacks by Dropping Treatment or Taking Low Doses
Thousands of statin users worldwide are suffering preventable heart attacks, simply because they are not complying with their treatment or are taking too low a dose, according to new research.
Study: Low-Protein, Low-Calorie Dieters Have Reduced Levels of Hormone Linked to Cancer
Preliminary findings suggest that eating less protein may help protect against certain cancers that are not directly associated with obesity.
Australian Study: Pharmacists Likely to Play Direct Role in Future Diabetes Management
Community pharmacists could soon be playing a more direct role in diabetes management following a new study at Brisbane's Wesley Research Institute funded by the MBF Foundation.
Discovery of a Critical Role for Sensory Nerves in Diabetes Opens Door to New...
Discovery has led to new treatment strategies for diabetes, achieving reversal of the disease without severe, toxic immunosuppression.
Kidney Blood Flow Changes May Explain Increased Long-Term Risks for Overweight Kidney Donors
Living kidney donors who are overweight or obese have increased blood pressure within the remaining kidney—which could explain the increased long-term risk of kidney damage previously found in this group of donors.
Job Burnout May Make People More Prone to Developing Diabetes
An Israeli study suggests that people who suffer from job burnout may be prone to developing a form of diabetes.