Researchers have announced an amazing new technology for people with diabetes that could allow blood-glucose level testing via a non-invasive contact lens that samples glucose levels in tears.
Blood testing is the standard option for checking glucose levels, but a new, non-invasive technology could allow testing via a contact lens that samples glucose levels in tears.
“There’s no noninvasive method to do this,” said Wei-Chuan Shih, a researcher with the University of Houston who worked with colleagues at UH and in Korea to develop the project, described in the journal Advanced Materials. “It always requires a blood draw. This is unfortunately the state of the art.”
But glucose is a good target for optical sensing, and especially for what is known as surface-enhanced Raman scattering spectroscopy, said Shih, an associate professor of electrical and computer engineering whose lab, the NanoBioPhotonics Group, works on optical biosensing enabled by nanoplasmonics.
This is an alternative approach, in contrast to a Raman spectroscopy-based noninvasive glucose sensor Shih developed as a Ph.D. student at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. He holds two patents for technologies related to directly probing skin tissue using laser light to extract information about glucose concentrations.
Continue Reading Below ↓↓↓
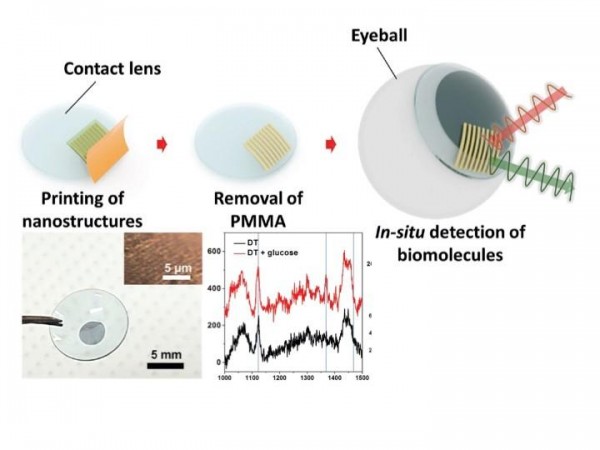
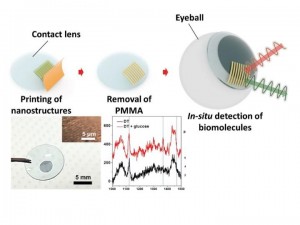
The paper describes the development of a tiny device, built from multiple layers of gold nanowires stacked on top of a gold film and produced using solvent-assisted nanotransfer printing, which optimized the use of surface-enhanced Raman scattering to take advantage of the technique’s ability to detect small molecular samples.
Surface-enhanced Raman scattering – named for Indian physicist C.V. Raman, who discovered the effect in 1928 – uses information about how light interacts with a material to determine properties of the molecules that make up the material.
The device enhances the sensing properties of the technique by creating “hot spots,” or narrow gaps within the nanostructure which intensified the Raman signal, the researchers said.
Researchers created the glucose sensing contact lens to demonstrate the versatility of the technology. The contact lens concept isn’t unheard of – Google has submitted a patent for a multi-sensor contact lens, which the company says can also detect glucose levels in tears – but the researchers say this technology would also have a number of other applications.
“It should be noted that glucose is present not only in the blood but also in tears, and thus accurate monitoring of the glucose level in human tears by employing a contact-lens-type sensor can be an alternative approach for noninvasive glucose monitoring,” the researchers wrote.
“Everyone knows tears have a lot to mine,” Shih said. “The question is, whether you have a detector that is capable of mining it, and how significant is it for real diagnostics.”
In addition to Shih, authors on the paper include Yeon Sik Jung, Jae Won Jeong and Kwang-Min Baek, all with the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology; Seung Yong Lee of the Korea Institute of Science and Technology, and Md Masud Parvez Arnob of UH.
Although non-invasive glucose sensing is just one potential application of the technology, Shih said it provided a good way to prove the technology. “It’s one of the grand challenges to be solved,” he said. “It’s a needle in a haystack challenge.”
Scientists know that glucose is present in tears, but Shih said how tear glucose levels correlate with blood glucose levels hasn’t been established. The more important finding, he said, is that the structure is an effective mechanism for using surface-enhanced Raman scattering spectroscopy.
Although traditional nanofabrication techniques rely on a hard substrate – usually glass or a silicon wafer – Shih said researchers wanted a flexible nanostructure, which would be more suited to wearable electronics. The layered nanoarray was produced on a hard substrate but lifted off and printed onto a soft contact, he said.
Continue Reading Below ↓↓↓
Source: University of Houston
Photo Credit: University of Houston
Journal: Advanced Materials