Researchers report the development of “sugar sponges” that sop up and release glucose as needed and it’s use as a treatment for both type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
Many diabetes patients must inject themselves with insulin, sometimes several times a day, while others take medications orally to control blood sugar. The injections, as well as the side effects from both regimens, can be painful.
Now, one team reports in the Journal of the American Chemical Society progress toward an insulin-free diabetes treatment that requires fewer injections.
According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, current trends predict that one in three adults in the U.S. will have diabetes by 2050. Treatments include insulin injections, which can be painful. In addition, the injections can involve different types of insulin — a slow-acting one before bed or a fast-acting one before meals — which can be confusing.
Pills are not much better, as patients sometimes forget to take them. Both drugs and injections can have various side effects, including nerve damage, infections and insulin resistance.
Continue Reading Below ↓↓↓
Non-invasive insulin-dependent systems that include hydrogels and polymers have developed in the laboratory, but they also can trigger these complications. So Jianzhong Du and colleagues wanted to develop a method that would be easy to use and that would avoid side effects.
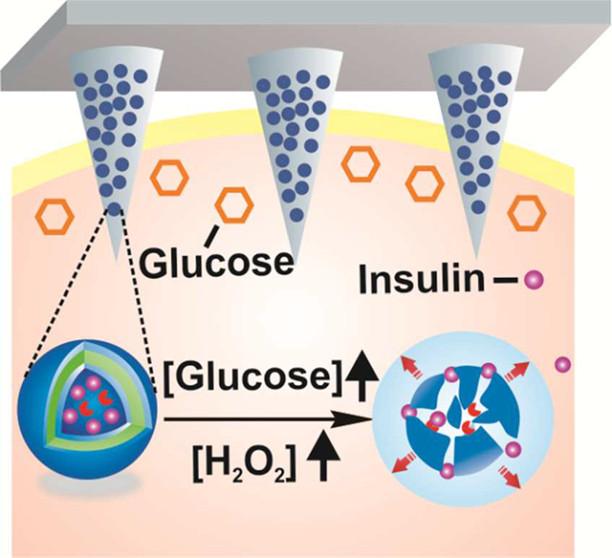
The researchers nicknamed their treatment the “sugar sponge.”
It’s an injected lectin-coated polymer vesicle that sopped up and bound glucose when glucose levels were high, and released the sugar when its concentrations were low in laboratory tests.
They also tested the sponge in mice with type-1 diabetes, and within two days, they saw antidiabetic effects.
The researchers say that the sponge could one day serve as a treatment for either type-1 or type-2 diabetes.
The authors acknowledge funding from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Shanghai International Scientific Collaboration Fund, Thousand Talents Plan (China) and the Fundamental Research Fund for the Central Universities. The abstract that accompanies this study is available here.
The American Chemical Society, the world’s largest scientific society, is a not-for-profit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS is a global leader in providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple databases, peer-reviewed journals and scientific conferences. ACS does not conduct research, but publishes and publicizes peer-reviewed scientific studies. Its main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
Source: American Chemical Society
Journal: Journal of the American Chemical Society
Citation:
Sugar-Breathing Glycopolymersomes for Regulating Glucose Level
Yufen Xiao, Hui Sun, and Jianzhong Du
Journal of the American Chemical Society Article ASAP
DOI: 10.1021/jacs.7b03219